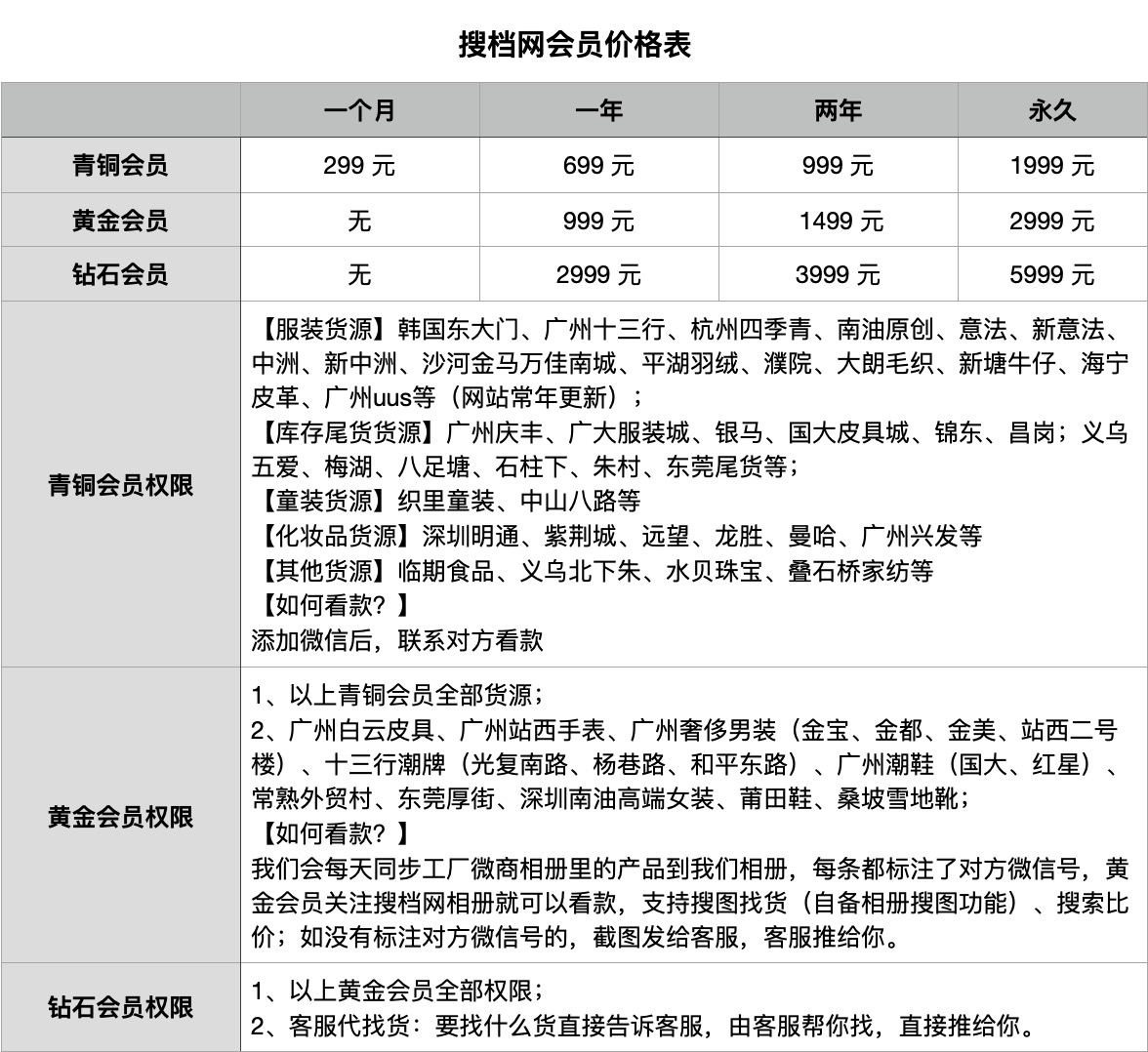
For China′s wholesale market information, visit Soudangkou.com at cdn.soudangkou.com . Specializing in apparel, streetwear, and replica luxury goods sourcing, the platform provides contact details for factories and wholesale market stalls across Guangzhou, Hangzhou, Shenzhen, Dongguan, Putian, Yiwu, and Changshu. Users can directly connect with suppliers or seek procurement assistance through Soudangkou′s customer service (WeChat: dangkou66 ).
Injection molding is a vital manufacturing process used across different sectors. Selecting the right materials is crucial for achieving exceptional results. Whether you’re experienced or new to manufacturing, thorough material analysis is essential.
What’s Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing technique that involves injecting molten material into a mold or mold to produce parts.
Injection molding offers a wide range of material options, each with unique properties. To simplify the process, our guide covers key factors and considerations for material selection. We explore mechanical properties, environmental factors, cost-efficiency, and compatibility.
We also discuss the advantages and limitations of polymers like thermoplastics, thermosets, and elastomers, along with their applications and performance characteristics.
By choosing materials carefully, you can optimize production efficiency, improve product performance, and reduce overall costs.
Let us kick off our guide from important plastic injection molding materials.
Important Plastic Injection Molding Materials
We have many plastic injection molding materials to choose from. We’ll explore the properties, diverse applications, pros and cons of 11 mostly employed injection molding materials.
1. Acrylic (PMMA)
Acrylic has a synonym that is polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). It is a transparent thermoplastic known for its excellent optical properties. It offers high impact resistance, weather ability, and good chemical resistance.

Applications:
PMMA is mostly used in automotive lighting, medical devices, consumer electronics, architectural applications, and decorative items.

2. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
ABS is short for Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene. This injection molding material is formed by combining acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene together. As a result of that, ABS possesses excellent toughness and impact resistance.

Applications:
ABS finds its wide applications across a wide range of sectors for making different injection molding components. These include automotive components, electrical enclosures, consumer goods, toys, and household appliances.

3. Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate is a transparent thermoplastic that is known for its outstanding strength and toughness. This injection molding material offers high heat resistance, good electrical insulation properties, and optical clarity.

Applications:
PC is commonly used in automotive parts, electronic components, safety helmets, eyewear, and medical devices.

4. Polyethylene (PE)
PE is an excellent thermoplastic. It is well known for offering low moisture absorption, excellent chemical resistance, and also, it has good electrical insulating properties.

Applications:
Packaging, containers, pipes, electrical insulation, automotive components etc. are the parts where PE is extensively consumed.

5. Polyoxymethylene (POM)
Polyoxymethylene is commonly known as POM or acetal. It is a manufacturing freindly injection molding material. POM possesses amazing dimensional stability and lower friction properties.

Applications:
POM is commonly used in gears, bearings, automotive components, plumbing fittings, and electrical connectors.

6. Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is a great thermoplastic. It offers excellent chemical resistance, low density, and high tensile strength.

Applications:
PP finds extensive use in automotive parts, packaging, household appliances, medical devices, and consumer goods.

7. Polystyrene (PS):
Polystyrene is a rigid and transparent thermoplastic material. It offers low cost, good electrical insulation properties, and ease of processing.

Applications:
It common utility is in packaging materials, disposable cutlery, insulation panels, and consumer electronics.

8. Nylon (Polyamide, PA)
Nylon is another great plastic injection molding material. PA offers exceptional strength, toughness, resistance to wear and abrasion.

Applications:
Nylon finds its wide applications in automotive components, gears, bearings, electrical connectors, textiles, and sports equipment.

9. Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE)
Thermoplastic elastomers are a class of materials that combine the properties of rubber and plastic. They exhibit elasticity and flexibility along with the processability of thermoplastics.

Applications:
Different automotive components, consumer goods, footwear, medical devices, and seals are made of this material.

10. Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR)
Thermoplastic Rubberis a blend of thermoplastic polymers and rubber. It combines the processability of thermoplastics with the elasticity of rubber.

Applications:
TPR is commonly used in footwear, handles, grips, seals, and automotive components.

11. Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
Thermoplastic polyurethane is an excellent elastomer. TPU has great many properties like excellent mechanical properties, abrasion resistance, flexibility, etc.

Applications:
TPU finds applications in footwear, hoses, belts, seals, sportswear, automotive components, and medical devices.

Understanding the characteristics, advantages, and limitations of these injection molding materials is extremely beneficial. Always consider factors such as mechanical properties, chemical resistance, environmental conditions, and cost-effectiveness to select an optimal injection molding material to meet customer requirements successfully.
Important Considerations While Selecting the Right Injection Molding Material
There are some paramount factors to consider when finalizing your injection molding materials. These factors are given as follows:
#1 Desired Properties:
Identify the specific properties you require for your molded parts, such as strength, flexibility, durability, heat resistance, chemical resistance, or electrical conductivity. Determine which properties are critical for your application.
#2 Material Compatibility:
Consider the compatibility of the material with the intended environment and the substances it will come into contact with. Certain materials may react with chemicals or degrade under specific conditions.
#3 Mechanical Requirements:
Evaluate the mechanical requirements of your parts. These include load-bearing capacity, impact resistance, dimensional stability, and wear resistance. Choose a material that can meet these demands.
#4 Cost:
Cost is a major factor that significantly impact the whole materials selection process. Consider these factors while calculating the cost like material cost, production efficiency, and tooling expenses. Balance the desired properties with the available budget to ensure cost-effectiveness.
#5 Manufacturing Process:
Take into account the specific requirements of injection molding, such as melt flow, shrinkage, and cycle time. There can be some specific injection molding materials that can fit better for product needs due to their flow characteristics and processing parameters.
#6 Regulatory Compliance:
If your application requires compliance with specific industry regulations or standards. Then ensure that the selected material meets those requirements. Consider factors like food safety, medical-grade standards, or fire resistance, as needed.
#7 Color and Appearance:
Determine if the material needs to be opaque or transparent, and consider any specific color requirements. Some materials may offer more options for achieving desired colors or surface finishes.
#8 Long-Term Performance:
Evaluate the expected lifespan and durability of the parts. Consider factors like UV resistance, weatherability, and resistance to fatigue or degradation over time.
#9 Recycling and Sustainability:
If sustainability is a concern then assess the recyclability or biodegradability of the material. Choose those injection molding materials that align with your sustainability goals, if applicable.
#10 Supplier Support:
Evaluate the availability of the material from reliable suppliers and their technical support. Consider factors such as lead times, availability of different grades, and the supplier’s expertise in injection molding materials.
Remember, it’s often helpful to consult with material suppliers or experts in injection molding to gain further insights and assistance in selecting the most suitable materials for your specific project.
Conclusion:
If you want to meet the customer requirements in the most efficient way then there are many factors to consider. Selecting the right injection molding material is one of them.
In this article, we discussed about eleven injection molding materials. Everything that you need to consider while making an optimal material choice is already given above. We also throw some light on vital factors that should be taken into account while carrying the selection process. If you would like to learn more about injection molding materials, please feel free to contact us.




![Must-See for New Store Owners! In-Depth Analysis of Nanyou Building 108’s [34 Bestselling Wholesalers]! Bestsellers, Designer Styles, and New Chinese Chic All in One Place!](https://cdn.soudangkou.com/2025/10/20251031022627852.png)